Rest Assured - Journey to the end to end API automation
Written by Rahul Pandey
October 31, 2022 — 8 Min Read | 0 Comments
REST Assured is a Java-based library, one of the most popular libraries to test RESTful Web Services, and is used to perform testing and validation of Rest Services with simplicity. We can use any Java IDE for writing code to test our API. REST Assured is helpful in writing small Unit tests as well as large automation frameworks, where we can create test cases for large APIs.
We can create highly customizable HTTP Requests to send to the Restful server. This enables us to test a wide variety of Request combinations and in turn test different combinations of core business logic.
What are the Usecases and Benefits of API Automation?
Use-Cases:
Good API Coverage
We’ve automated the end-to-end flow of our Application using REST Assured, we’ve covered test data creation and test case validation, so we’ve got a good API coverage that helps us to ensure the basic flow is maintained throughout. Once the latest feature is deployed, after manual testing we add the changes to our API test suite and keep it up to date so that it'll help us in regressive testing also in case of any updates of the same feature, we run automation test during staging, make necessary additions and ensure the flow of the application, which makes our API framework robust.
Separation b/w Frontend and Backend Testcases
Frontend testing includes the verification of the application and checks the performance of application whether it is working according to the requirement whereas Backend testing execution makes sure that the data is continuing as there is no performance hit, the deciding factor here are as follows :
- The tester should ask “Am I testing the UI, or Am I testing through the UI ?". If the answer is the latter, it should be covered in API.
- We add negative test cases through API automation and validate the status code.
- Logic which is in Frontend Codebase goes into FE/UI test suite and the logic from the Backend Codebase goes to the API test suite.
Removal of Runscope dependency
Before REST Assured we were using Runscope for API testing, it was good, but it had certain pitfalls primarily because it was hard to maintain, difficult to configure for running the test cases, and due to the complexity it came up with, the contribution from new team members was low, Whereas REST Assured is free, Open Sourced, easy to understand and contribute which made us migrate our test-cases to it, REST Assured solved the problem and increased our overall performance.
REST API Testing Open Source Framework
Salient features are as follows :
- It is Wingify’s open source framework that provides solution to automate Rest API Test cases at a go.
- Gives flexibility to the user to use the core structure of this framework, to automate users’ REST APIs by adding his own code on top of it.
- It consists of Basepackage, which has 2 classes, BaseApi and BaseTest. BaseApi class contains all the wrapper methods over RestAssured and BaseTest class contains the pre-requisite and post requisites for our test classes.
- This framework provides user the capability to log Curls for all your API requests which can help you debug incase of any issues.
- It also provides listeners and reports for better understanding of your test results.
Language independent
The exchange of data in APIs takes place in a structured format of either XML or JSON, which makes it language-independent and gives us the flexibility to choose any language for automation, we at Wingify are using JSON because it is faster and designed specifically for data interchange.
Benefits:
Ease in automation
API automation is used to monitor the backend of an application. API testing is effectively automated because the endpoints and request parameters are less likely to change unless there is a major change in business logic. Automation reduces manual efforts during regression testing and results in a significant amount of time-saving. As a result, the testing process is faster with better coverage. This culminates in time and resource-saving. Overall, it translates into the reduced project costs.
Improved test coverage
API test automation helps in covering a high number of test cases, functional and non-functional. Also, for a complete scenario check API testing requires running both, positive and negative tests. Since API testing is a data-driven approach, various combinations of data inputs can be used to test such test cases, we use ‘dataProviders’ annotations for inputting data of wide range. This gives good test coverage overall. Good test coverage helps in identifying and managing defects in a larger scenario. As a result, minuscule bugs make their way to production, thus resulting in a higher-quality product. We've 95% test cases coverage with API Automation, which gives us the confidence to push failures as alerts which couldn't have been possible with Protractor/ FE Automation due to flakiness.
Easy to maintain
API tests are usually deemed stable and major changes are done mainly when business logic is changed. The frequency and amount of changes are comparatively less. This means less rework in rewriting test cases in event of any changes. This is in sharp contrast to UI testing, which requires rework at many levels in case of any changes. API tests can be reused during testing, thus, reducing the overall time quantum required for testing.
Identifies and rectifies Business logic bug
APIs represent specific business logic, it is easier for the teams to isolate the buggy module and rectify it. The bugs reported early can be fixed and retested, independently yet again. This reduces the quantum of time taken between builds and release cycles, resulting in faster release of products.
The amount and variety of input data combinations inadvertently lead to testing limit conditions that may not be identified/tested otherwise. This exposes vulnerabilities, if any, at an earlier stage even before UI has been developed. These vulnerabilities can then be rectified on a priority basis and any potential loophole for breaches is handled. When there are multiple APIs from different sources involved in the development of an application, the interface handshake may or may not be firm. API testing deep dives into these integration challenges and handles them at earlier stages. This ensures that the end-user experience is not affected because of the issues that could have been dealt with at the API level.
What does our Architecture look like?
Our Architecture is classified into 3 parts
1. TestClass
Almost every class extends BaseTest Class that helps us to log in before test class execution & logout once the test class gets executed
We use the ‘TestUtilFunctions’ class to perform operations like validating the status code, fetching JSON value from the Response, validating the JSON schema
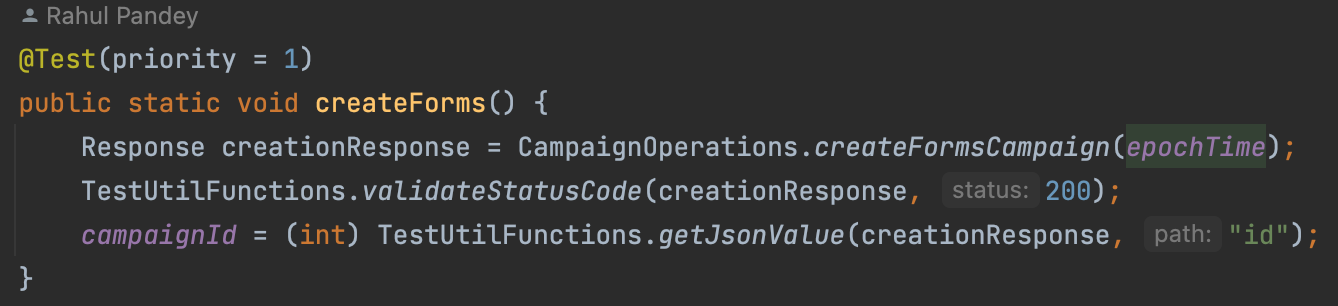
2. HelperClass
It creates an object of BaseApi class ( BaseApi Class which deals with cookies, header map, and request parameters from the builder class)
It sets Method Type(Get, Post, Patch, Delete), Basepath, and endpoints, and then returns the response to the Test class for validation
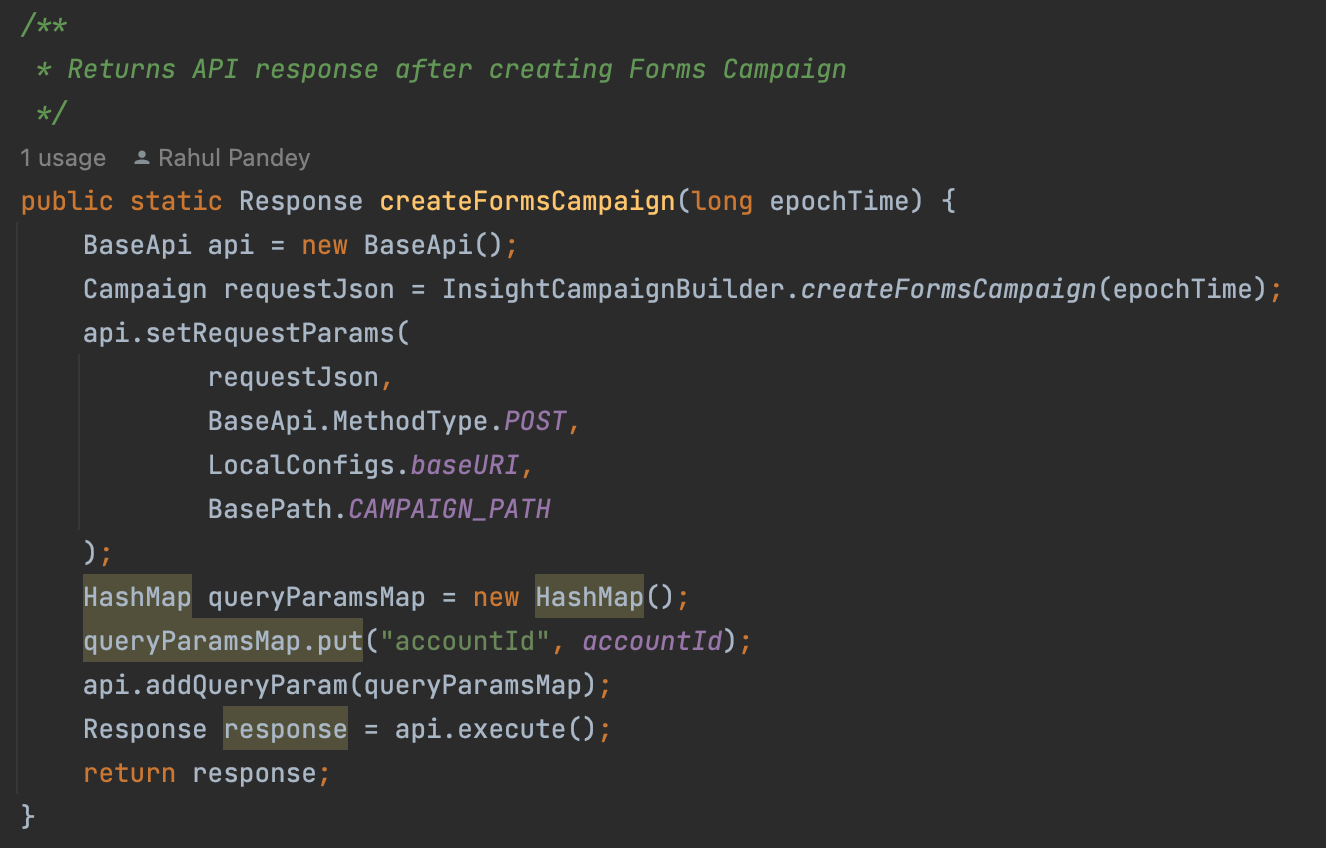
3. BuilderClass
The main purpose of a builder class is to create, customize and send requests JSON for POST and PATCH calls. The requested data is used is then used by the helper class to edit the endpoints as per the need.
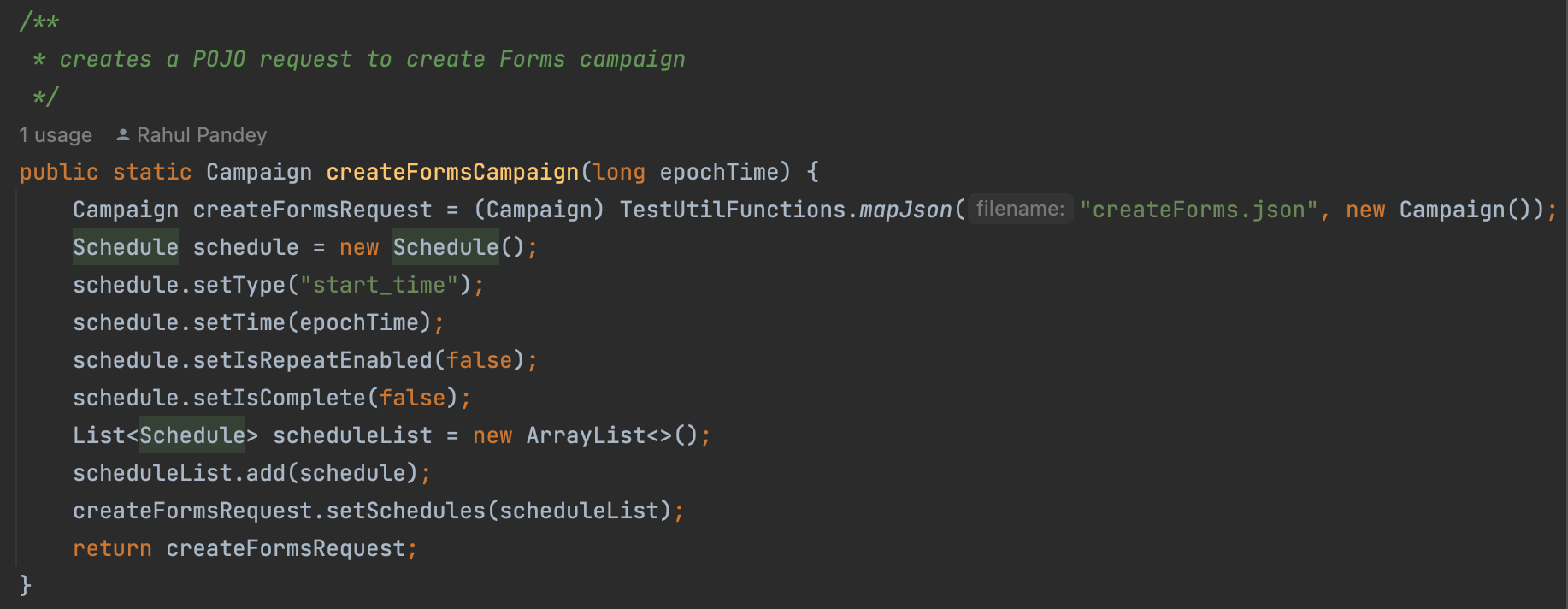
Other important parts of the architecture
4. POJO (plain old java object)
The POJO class is created to use the objects in other Java Programs. The major advantage of the POJO class is that we will not have to create objects every time in other Java programs. Simply we can access the objects by using the get() and set() methods.
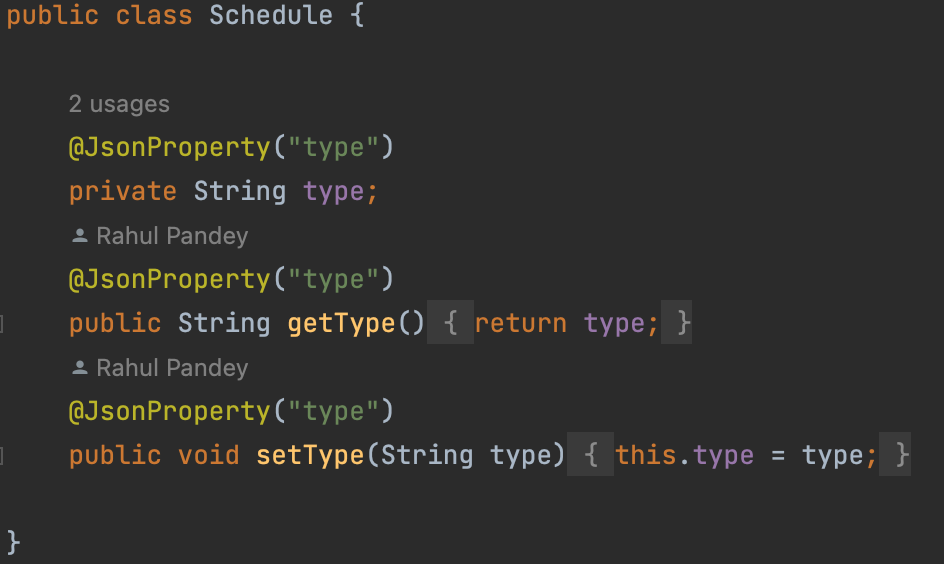
5. Execution
We use Gradle for the execution of our test cases. Gradle is an open-source build automation tool that is designed to be flexible enough to build almost any type of software. A build automation tool is used to automate the creation of applications. The building process includes compiling, linking, and packaging the code. The process becomes more consistent with the help of build automation tools.
6. Reports
We use ‘Extent Reports’ to display the reports of our executed test cases.
In the automation framework, reporting is a very important part where we can see the consolidated output of our all tests. An easily readable report with all the necessary parameters always helps to debug faster. Extent report is a reporting framework that we can add to our existing test framework.
It supports the below features over a traditional reporting framework:
- Customize our reports as per need.
- Provides a graphical representation and also a fancy look.
- Support for search.
- Support for filter based on status (PASS/FAIL/SKIP).
- Categories result based on an exception.
- Categories tests if there are multiple test suites/test cases.
- View total test count, start/end time, and total time is taken.
- Print the exceptions for failed cases.
- Allows capturing a screenshot.
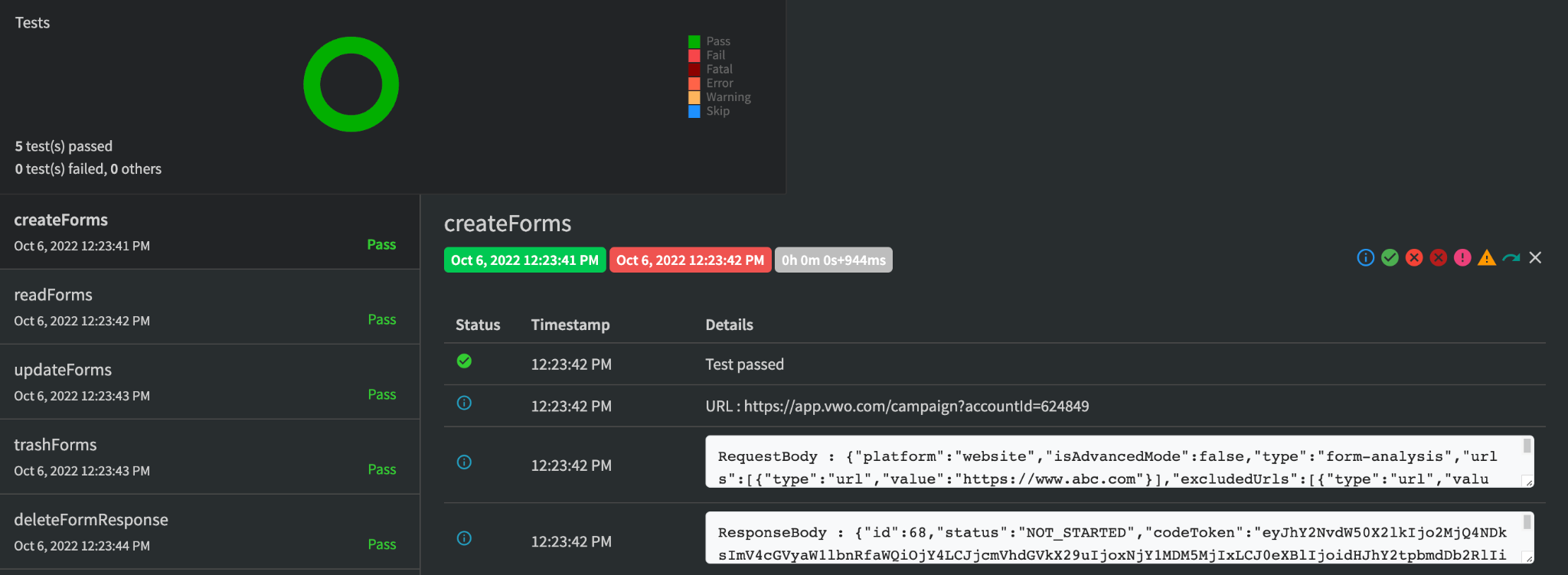
If a test case fails below details should display in the report:
- Test class name, Test name
- URL
- Request payload
- Response
- And all the input parameters passed from CSV
So it becomes easy for the Tester to identify the issue and the root cause of the issue
7. Testsuites
It is a collection of test cases that are intended to be used to test a software program to show that it has some specified set of behavior
A suite is represented by one XML file. It can contain one or more tests and is defined by the
A test is represented by
A TestNG class is a Java class that contains at least one TestNG annotation. It is represented by the
A test method is a Java method annotated by @Test in the source.
For Eg: Testcases revolving around A/B, MVT, Split, and Mobile A/B will be part of one suite, similarly, Goals, Funnels, and Heatmaps will be part of another one
Conclusion
APIs evolve and develop as and when business and functional requirements change, thus making it even more important to test them on a continuous basis. API test automation helps in covering a high number of test cases, functional and non-functional. Also, for a complete scenario check API testing requires running both, positive and negative tests. Since API Testing is a critical part of any development life cycle, REST Assured Framework is one of the most widely used Web Services Testing tools in Java. Advanced features, along with simplicity in implementation, make it a must for any testers to ensure quality in the end product. With its fluent approach and the expressive method names, it makes the call .

